Freelance Taxes has been a topic of high debate for the past few years with the popularity and rise in this field. Freelancing offers a world of opportunities for those seeking independence, flexibility, and control over their work life.
Whether you are a seasoned freelancer or just starting, it’s essential to have a solid grasp of the tax implications that come with this career path. Taxes for freelancers can be complex, but fear not!
This guide will provide you with a step-by-step breakdown of everything you need to know about freelance taxes. From understanding different tax classifications to maximizing deductions, we’ve got you covered. So, let’s dive into it without any further ado!
What is Freelancing?
Freelancing is a type of self-employment where individuals offer their services to clients or companies without committing to a long-term contract. Freelancers enjoy the freedom to choose their projects, clients, and work schedule. They decide their mode of work and have independency over each aspect.
Understanding Taxes for Freelancers
Freelancers are considered self-employed individuals, which means they are responsible for paying taxes on their income.
Unlike employees who have taxes withheld from their paychecks, freelancers must set aside a portion of their earnings to cover their tax obligations. These stats show the number of self-employers who paid taxes in Spain every month.
Freelancing and Taxes Explained
Understanding freelance taxes is not a big fish to catch. Let’s delve into the basics of freelance taxes to lay the groundwork for a deeper understanding of the topic.
Types of Taxes Freelancers Should Be Aware of
Taxes have a lot of kinds but does a freelancer must know all those types? No!
Freelance taxes are a little different. You only have to understand freelance taxes types to go well along your tax procedures. So let’s learn about the essential freelance taxes types below.

Income Tax
Income tax is the most common tax that freelancers need to pay. It is calculated based on their net income after deducting eligible expenses.
Self-Employment Tax
Freelancers are also required to pay self-employment tax, which covers Social Security and Medicare taxes. This tax is in addition to income tax and is calculated based on a percentage of the freelancer’s net earnings.
Estimated Tax Payments
Since freelancers do not have taxes withheld from their income, they need to make estimated tax payments throughout the year to avoid penalties and interest.
Sales Tax
Depending on the type of services or products offered, freelancers may also need to collect and remit sales tax.
Freelancer Tax Obligations
Let’s dive into the essential tax obligations every freelancer must fulfill to remain compliant with the IRS or any government agency operating with taxes in your region.
Registering for an EIN (Employer Identification Number)
Learn about the significance of obtaining an EIN and how to apply for one online. EIN application procedure is different for every region. So you must go with the one that is acceptable and working in your region.
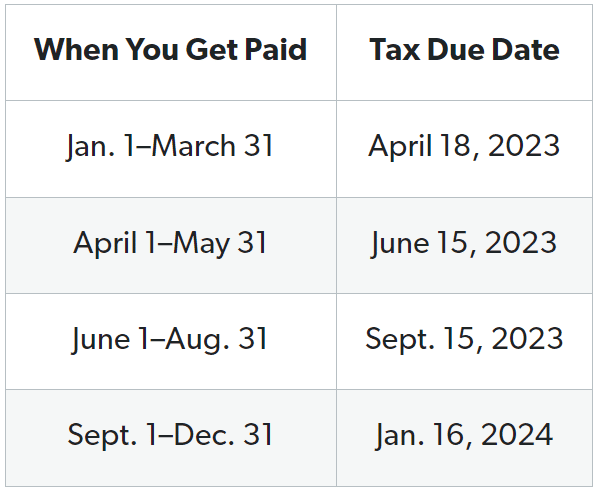
Quarterly Tax Payments for Freelancers
Freelancers are required to make quarterly estimated tax payments to the IRS, which helps in evenly spreading their tax obligations. Calculate these payments and avoid penalties.
Here’s the estimated calculation for the year 2023.
Understanding Self-Employment Tax
Discover the self-employment tax, what it entails, and how it differs from regular income tax in your region. This will aid you in your tax-paying procedures.
Record Keeping for Freelancers
Maintaining accurate and organized financial records is essential for freelancers to ensure smooth tax preparation and to claim eligible deductions. Here’s how you can keep a record of your expenses as a freelancer.
Separate Business and Personal Expenses
Freelancers should have separate bank accounts and credit cards for business and personal expenses to simplify record-keeping. It’ll not complicate their savings and earnings.
Expense Tracking
Tracking business expenses diligently allows freelancers to identify potential deductions and reduce their taxable income. It’ll aid in better planning. There are a lot of digital apps available in the market for keeping track of your expenses.
Invoicing and Receipts
Never lose a record of your invoices and receipts. They are essential and have to be saved. They serve as critical documentation for income and expenses, providing proof in case of an audit.

Deductions and Write-Offs for Freelancers
You head deduction? Yeah, you heard it right!
Claiming deductions is an effective way for freelancers to reduce their taxable income and lower their tax liability.
Here are the simple methods of deduction. You have to figure out the right one for you.
Home Office Deduction
Freelancers who use a portion of their home exclusively for work may qualify for a home office deduction. It means having no office and working at the ease of your home is a privilege.
Business Equipment
The cost of purchasing and maintaining business equipment can be deducted from the freelancer’s taxable income.
Travel and Transportation Expenses
Travel expenses incurred for business purposes, such as transportation and lodging, may also be deductible.
Understanding Tax Forms for Freelancers
Filing taxes as a freelancer involves specific forms. We’ll walk you through the most critical tax forms you need to know.
Form 1099-MISC
Learn about Form 1099-MISC and how it pertains to reporting your freelance income.
Form 1040-ES
Understand the purpose of Form 1040-ES and how it helps you estimate and pay your quarterly taxes.
Form Schedule C
Discover how to fill out Form Schedule C, which is used to report your profit or loss from freelancing.
Hiring an Accountant or Doing Taxes Yourself
If handling taxes seems overwhelming, hiring an accountant could be the right choice. Find out how an accountant can assist you with your tax responsibilities.
Deciding whether to hire a professional accountant or handle taxes independently depends on the freelancer’s comfort level with tax regulations and complexity.
Tax Deadlines and Extensions
Freelancers must be aware of tax filing deadlines and seek extensions if needed to avoid penalties. Not paying attention to deadlines can result in serious or complex consequences which you won’t want.
Managing Tax Payments and Avoiding Penalties
Paying taxes on time and accurately estimating tax payments are crucial for avoiding penalties and interest. In case you miss your deadlines for tax payments, you’ll be charged penalties that might disturb your expense and put you in a bad hole. So, to avoid penalties, stay tuned with your tax deadlines.

Tax Tips for Freelancers
Efficiently managing your freelance income and expenses is essential for a successful freelance career. Learn valuable tips for financial management.
Set Aside Money for Taxes
Saving a portion of each payment for taxes helps freelancers meet their tax obligations without financial strain.
Keep Up with Tax Law Changes
Tax regulations may change over time, and staying informed ensures compliance and potential tax-saving opportunities.
Take Advantage of Deductions
Maximizing eligible deductions can significantly lower a freelancer’s taxable income.
Tax Software and Tools for Freelancers
With the advancement in technology, there are a lot of tools available for managing taxes and other cores. They are utilizing tax software and online tools to simplify tax preparation and help freelancers stay organized.
Common Tax Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding these common tax mistakes can save freelancers from unnecessary stress and potential penalties.
Mixing Personal and Business Finances
Don’t ever mix your personal and business finances. Keeping personal and business finances separate is vital for accurate record-keeping.
Ignoring Deductions
Overlooking potential deductions means paying more taxes than necessary. That’s why it’s recommended to look for the correct deduction fits for you.
Late Tax Filings
Are you okay with losing a large portion of your earnings in penalties? No, right! Missing tax deadlines can lead to hefty penalties and interest charges. You have to avoid them at all costs by keeping yourself tuned with deadlines.
State Taxes for Freelancers
Freelancers must consider state taxes, which vary based on their location and the services they provide.
International Freelancing Taxes
Freelancers working internationally may encounter additional tax complexities, including tax treaties and reporting requirements.
FAQs
Do freelancers pay more taxes than regular employees?
No, freelancers do not pay more taxes than regular employees. However, they are responsible for paying both income tax and self-employment tax, which together can seem higher.
Can freelancers deduct their home internet expenses?
Yes, freelancers who use their home internet for work purposes can deduct a portion of their internet expenses as business expenses.
Are estimated tax payments the same for every freelancer?
No, estimated tax payments vary based on the freelancer’s income, deductions, and other financial factors.
How can freelancers find a reliable tax professional?
Freelancers can ask for recommendations from fellow freelancers or conduct research online to find a qualified tax professional.
Do I Need to Pay Taxes on Foreign Freelance Income?
Yes, you are required to report and pay taxes on your foreign freelance income.
What If I Miss the Quarterly Tax Payments?
If you miss the quarterly tax payments, you may be subject to penalties and interest. It’s crucial to make timely payments to avoid these consequences.
Can I Deduct Business Meals as Freelancer?
Yes, you can deduct certain business meal expenses as long as they are directly related to your freelance work.
What Records Should I Keep for Tax Purposes?
You should keep records of income, expenses, invoices, contracts, and any other documentation related to your freelance business.
Do I Need to Pay State Taxes as a Freelancer?
Yes, you may be required to pay state taxes based on your location and the states where you conduct business.
Summary of Freelance Taxes
Navigating the world of freelancing and taxes may seem daunting, but armed with the knowledge from this comprehensive guide, you can confidently tackle your tax responsibilities. Remember to keep accurate records, claim eligible deductions, and, if needed, seek professional guidance to ensure you remain compliant with tax regulations. As a freelancer, understanding taxes empowers you to make informed financial decisions and pave the way for a successful freelance career.

